Learn how compound interest works with simple examples, formulas, and tips to grow your money faster through the power of compounding.
It is one of the most powerful concepts in finance and is often called the “eighth wonder of the world.” Whether you are saving for the future, investing in mutual funds, or planning for retirement, compound interest can play a huge role in helping you achieve your financial goals.
Table of Contents
In this blog, we will explain compound interest in simple words and show you how it really works with a realistic example.
What is Compound Interest?
To understand the power of compounding, let’s first look at simple interest.
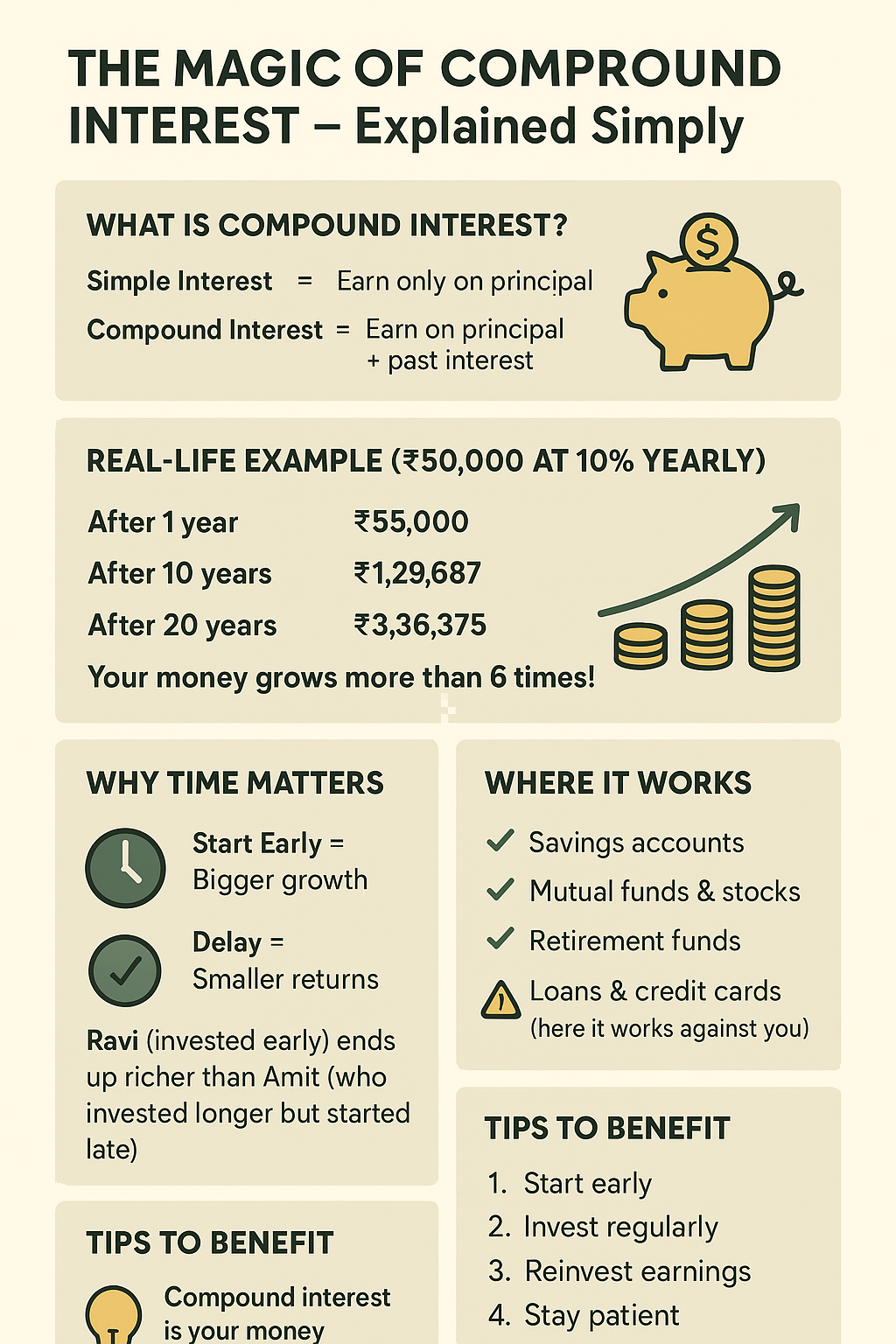
Simple interest means you earn returns only on the original amount (the principal). For example, if you invest ₹10,000 at 10% simple interest per year, you get ₹1,000 every year. After 5 years, the total becomes ₹15,000 (₹10,000 principal + ₹5,000 interest).
Now comes the difference.
With compounding, you earn not just on your starting amount but also on the interest you’ve already accumulated. This “interest on interest” creates a snowball effect — your money keeps multiplying because past gains also start earning returns.
This small shift makes a huge difference over time.
The Formula Behind Compounding
Here’s the formula, kept simple: A=P(1+r/n)ntA = P (1 + r/n)^{nt}A=P(1+r/n)nt
Where:
- A = final value (principal + interest)
- P = starting amount
- r = annual interest rate (in decimal form, e.g., 10% = 0.10)
- n = number of times interest is compounded in a year (quarterly = 4, yearly = 1, monthly = 12)
- t = time in years
You don’t need to memorize it. Just know that four things matter most:
- How much you start with (P)
- The interest rate (r)
- How often it compounds (n)
- Time (t)
Among these, time has the biggest impact. The longer you leave your money invested, the stronger compounding becomes.
A Real-Life Example
Suppose you invest ₹50,000 in a mutual fund that grows at 10% per year, compounded annually.
- After 1 year: ₹55,000
- After 2 years: ₹60,500
- After 3 years: ₹66,550
Notice how the yearly gain rises — not because you added money, but because the total itself is growing.
Over a longer period:
| Year | Total Value | Interest Earned That Year |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ₹55,000 | ₹5,000 |
| 5 | ₹80,525 | ₹7,320 |
| 10 | ₹1,29,687 | ₹11,789 |
| 15 | ₹2,08,697 | ₹19,065 |
| 20 | ₹3,36,375 | ₹30,559 |
So, after 20 years, your ₹50,000 becomes ₹3,36,375 — more than 6 times the original amount — without you adding a single rupee extra!
That’s the magic of compound interest.
Why Starting Early Matters
The earlier you begin, the more time your money gets to multiply.
- Ravi invests ₹5,000 per month from age 25 to 35 (10 years). He stops after that.
- Amit starts later, at age 35, and invests the same ₹5,000 per month for 20 years until age 55.
Assuming a 10% return:
- Ravi’s investment grows to about ₹1.1 crore by age 55.
- Amit’s grows to about ₹76 lakh — even though he invested for double the years.
Why the difference? Ravi’s money simply had more time to compound. money got more time to compound. Time is the most powerful factor in compound interest.
Where You See Compounding in Real Life
This principle shows up everywhere in personal finance:
- Public Provident Fund – pPF give compound interest on Investment.
- Mutual Funds & Stock Market – Returns get reinvested and generate fresh gains.
- Retirement Funds(PF and NPS) – they grow steadily with compounding.
- Loans & Credit Cards – here it works against you, as unpaid interest adds up quickly.
Tips to Benefit from Compounding
- Start Early – Even small amounts can grow huge if given time.
- Stay Consistent – Regular investments speed up growth.
- Reinvest Earnings – Let your returns work for you.
- Be Patient – It feels slow at first but accelerates later.
- Avoid Costly Debt – Remember, compounding can grow loans too.
Key Takeaway
Compounding is like a snowball rolling down a hill — it starts small but grows bigger and faster as it keeps rolling. The earlier you start, the more powerful it becomes.
Whether you’re saving for retirement, investing in mutual funds, or building wealth for future goals, understanding the power of compounding can help you make smarter money decisions.
The best time to begin was yesterday. The second-best time is today.